How to configure outgoing email filtering with SpamExperts?
Setting up SpamExperts to protect your organization's emails is not automatic. It requires several steps which we detail below.
>
It is important that you follow the steps properly to ensure that emails are correctly filtered by SpamExperts and that they are delivered optimally to your recipients.
>
If you use web hosting with Hodi, you don't need to do anything on your site as we include outbound filtering for free on all web hosting plans to protect you.
1. Log in to SpamExperts
- Log in to your client area
- In the "My Account" menu, choose "My Services"
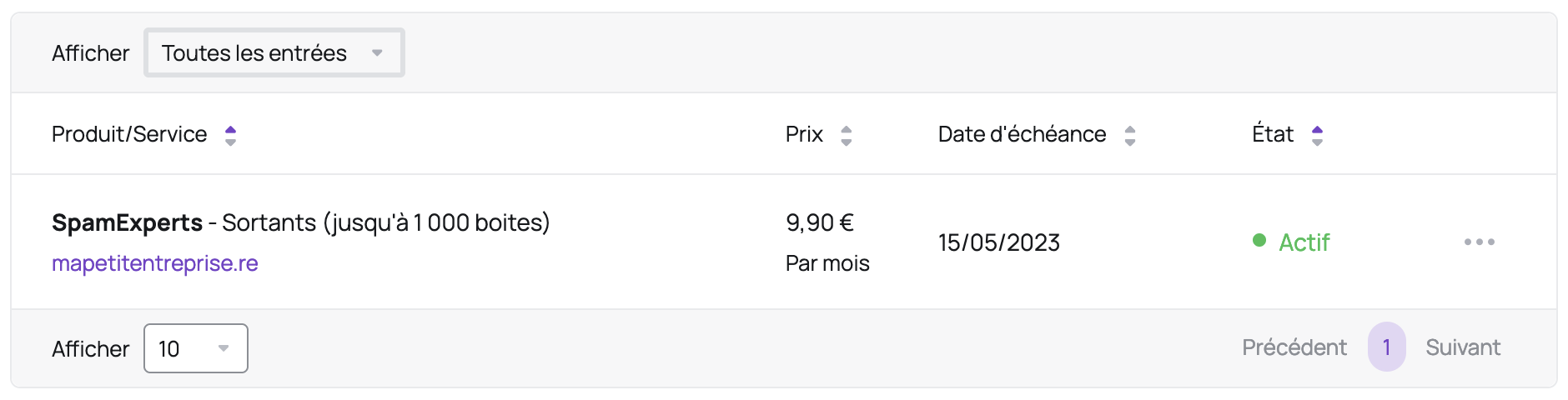
- Click on the "SpamExperts" line corresponding to the domain you wish to access:
- Click on "Log in to SpamExperts":
- If SpamExperts does not open, check that your browser is not blocking popup windows.
- If SpamExperts is in English, click on the "English (US)" button at the top right and choose "French":
2. Configure outbound email authentication
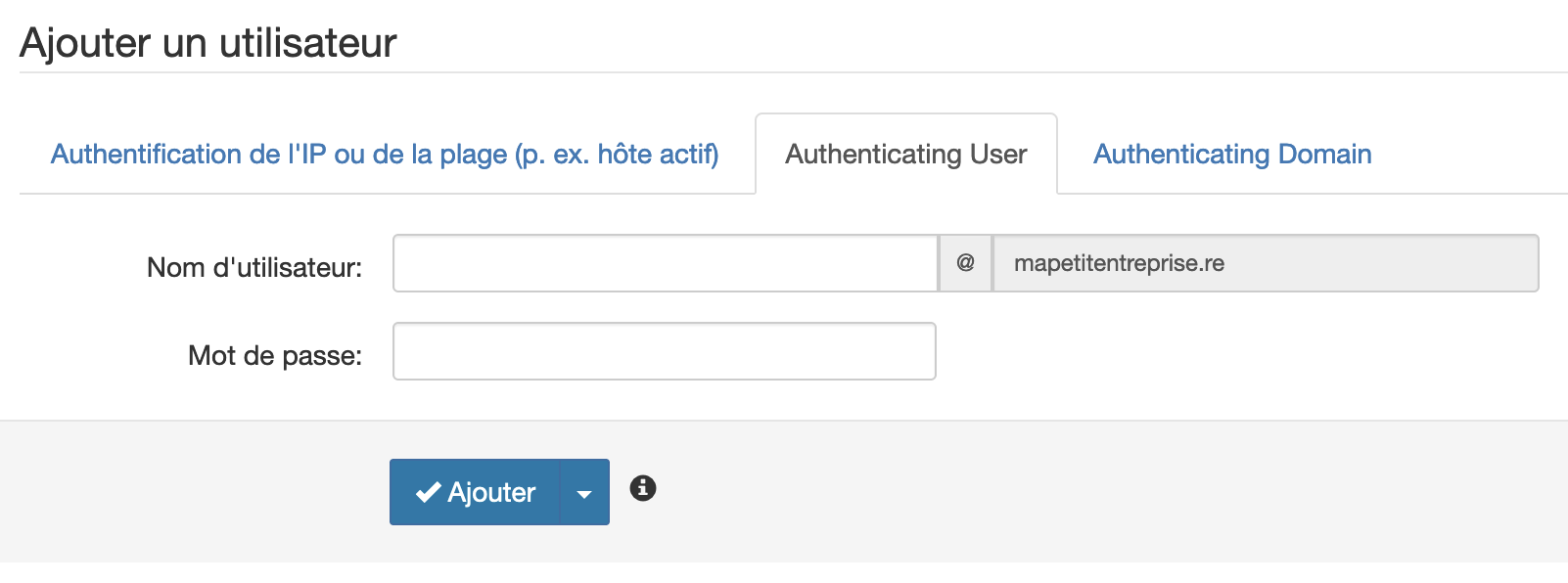
- In the left menu, choose "Manage users" in the "Outgoing" section
- Create a username and password that you will use on your SMTP server in the "Add a user" section:
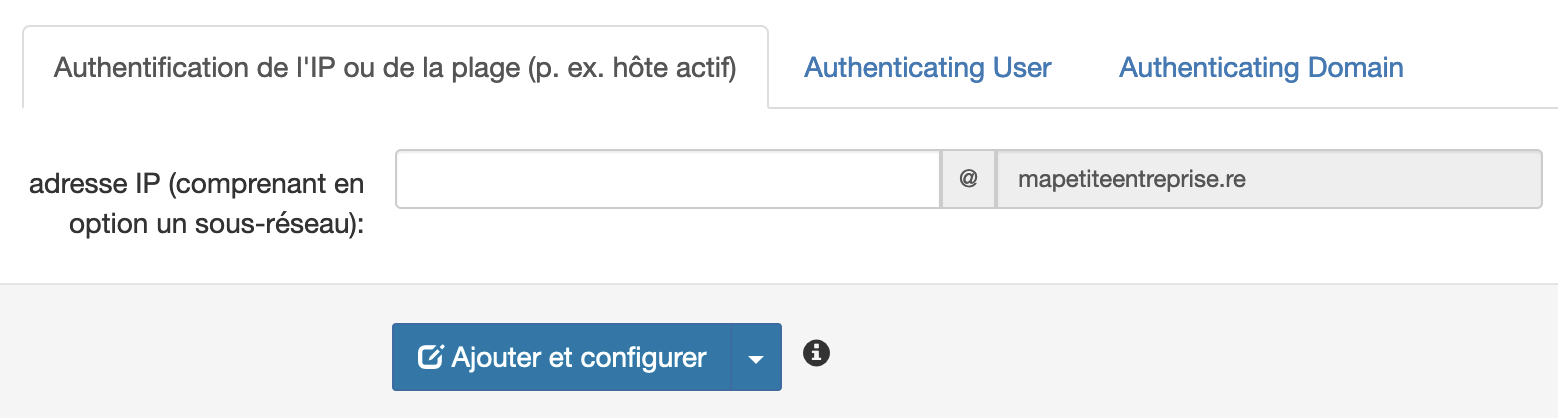
- You can also use IP address authentication if you have a static IP by clicking on "IP or range authentication (e.g. active host)":
3. Configure the blocking notification email
In order to be alerted of any blocks so you can take action at the source (e.g., clean a computer infected with a virus), you can enter the alert email address in the "Settings" menu of the "Outgoing" section.
4. Optimize your email delivery (SPF and DKIM)
- If you are not familiar with SPF and DKIM, you can learn more about SPF and DKIM.
- Add
include:spf.antispamcloud.comto your SPF record in your DNS zone (this is the TXT record that starts withv=spf1) - If your current record is
v=spf1 a mx include:spf.hodi.host -all, it will becomev=spf1 a mx include:spf.hodi.host include:spf.antispamcloud.com -all(for added security, please verify the new syntax with SPF Syntax Validator before saving) - If you do not have such a TXT record, you can create a new one containing
v=spf1 include:spf.antispamcloud.com -all(the record name is your domain name or@in some cases)
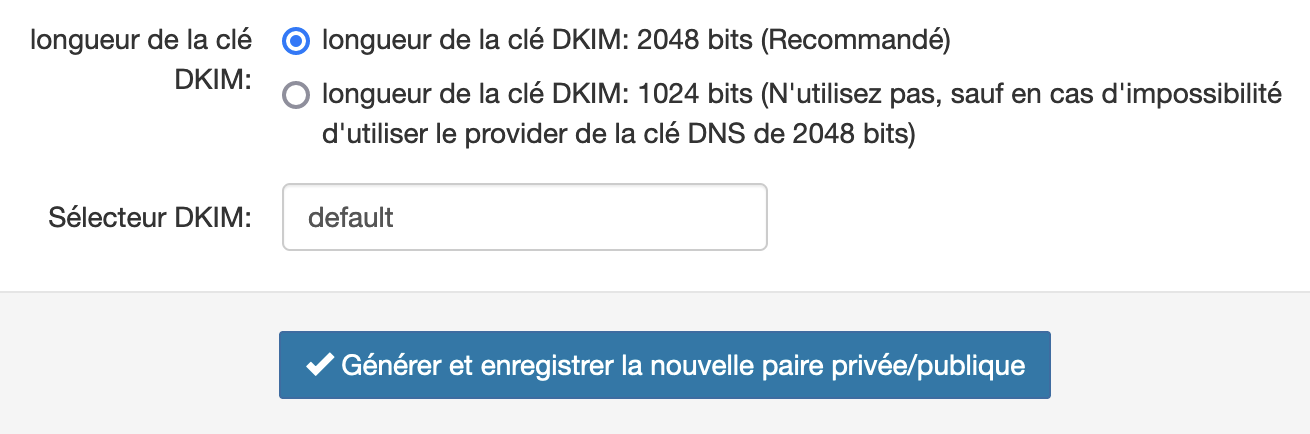
- If your server does not sign emails with DKIM, SpamExperts can do it for you. To do this:
- Go to the "DKIM" menu in the "Outgoing" section
- Enter a selector, for example
default:
- Create the DNS TXT record in your DNS zone with the content indicated, the record name being the DKIM selector you chose followed by
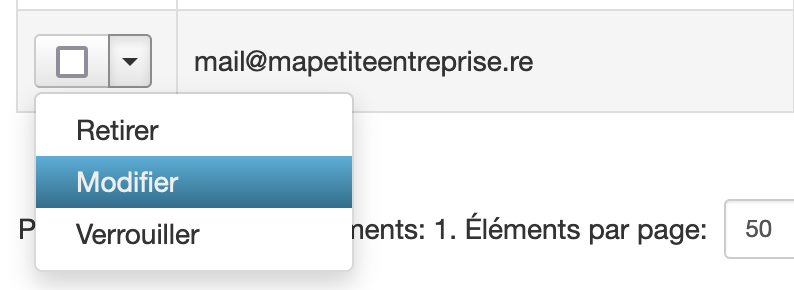
._domainkey.followed by your domain name, for exampledefault._domainkey.mapetiteentreprise.re: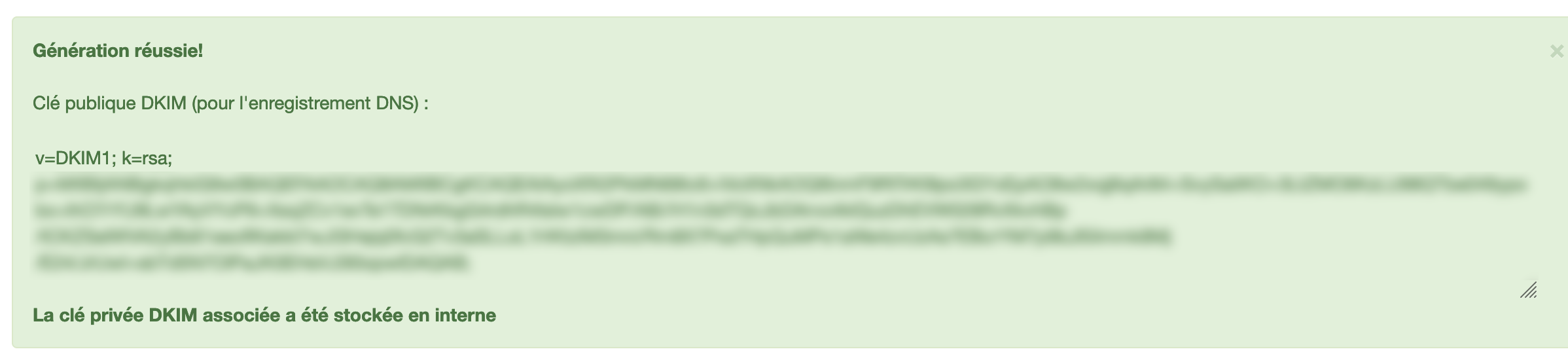 - If you use a selector other than
default, you must specify it in the user configured in step 2, by clicking on the arrow next to the checkbox then "Edit" (the field to modify is "DKIM Selector"):
Here are some guides from different hosting providers to help you edit your DNS zone:
- Hodi
- Canal+ Business: request from technical support
- Gandi
- IDOM: request from technical support
- Ionos
- Orange Business Services
- OVH
- SFR Business: request from technical support
If you have any questions about the exact procedure to edit the DNS zone at your hosting provider, we recommend contacting their technical support.
5. Configure your server to use SpamExperts
Once the steps above are completed, you are ready to use SpamExperts.
You can use one of the following domain names as an SMTP relay on port 587 (with or without TLS), 465 (SSL) or 25 (without SSL/TLS, not recommended).
- European Union:
eu.smtp.antispamcloud.com - South Africa:
za.smtp.antispamcloud.com
If you configured a username and password in step 2, you will need to use them in the SMTP relay configuration.
The SMTP relay in South Africa is more performant if you are with an ISP connected to South Africa, such as Zeop or SFR, but you may prefer to use a server in the European Union.
6. Secure your network
We finally recommend securing your network by blocking outgoing connections on port 25 (excluding your server if you use port 25 to reach the SpamExperts SMTP relay).
This will prevent compromised workstations from sending emails directly to another SMTP server without going through SpamExperts.
Warning: since the IP addresses used by SpamExperts are subject to change, you should not create a firewall rule to only allow traffic to those IP addresses. Instead, you should create a firewall rule to block traffic that does not originate from an authorized IP on your network.
7. Monitor outgoing emails
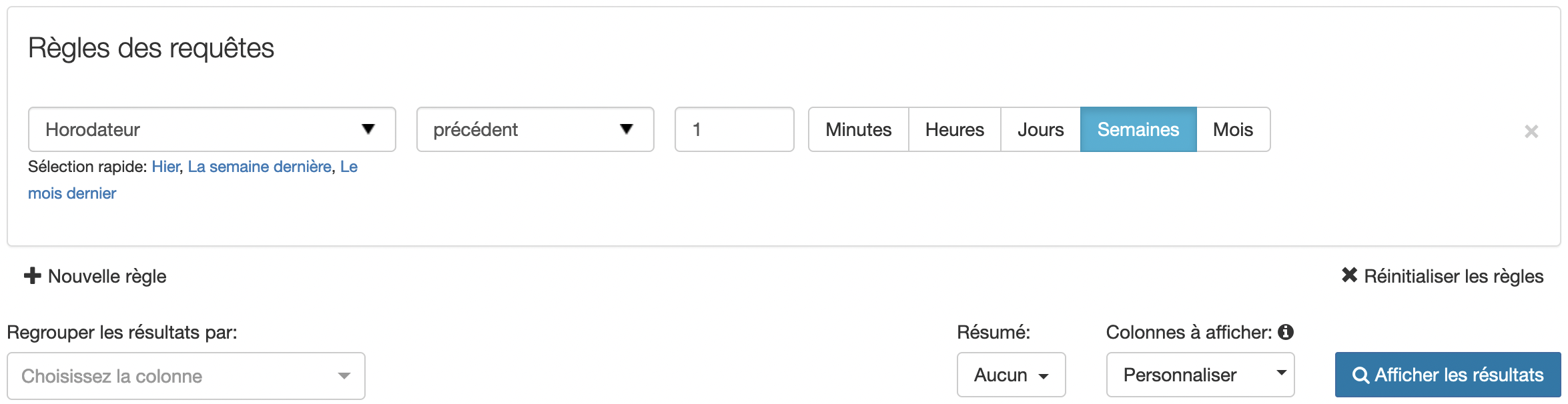
You can monitor emails passing through SpamExperts by going to the "Logs" menu in the "Outgoing" section.
It is mandatory to apply filters in this section using the "Query rules" section and clicking the "Show results" button. The default filter displays messages from the last week.
Once the filter is applied, the "Status" column indicates the message status. Here are the most common statuses:
delivered: the message was sent to the recipientqueuedorbounced: the message could not be sent to the recipient (you can click on the arrow next to the checkbox then choose "Delivery problem log" to learn more)queued: SpamExperts will periodically retry sending the messagebounced: the number of send attempts has been exceeded and SpamExperts sent an error message to the sender to inform them that the message could not be delivered
not-accepted: the message was not accepted, for example because the SMTP connection did not terminate correctly (the sender received an error message)rejected,quarantinedorquarantined-expired: the message is considered dangerous (spam or virus for example) and was blocked by SpamExperts; it was therefore not sent to the recipient. You can learn more by displaying the "Subcategory" and "Additional category" columns
Note: the SpamExperts time corresponds to the Paris time zone.
Unlike inbound filtering, a message determined to be dangerous by SpamExperts cannot be sent to the recipient (there is no tool available for this).
>
You will need to take into account the information displayed in "Subcategory" and "Additional category" to improve the quality of your message. For your information, even if SpamExperts allowed the email to pass through, there is a high chance it would be blocked by the recipient's server, which could lead to a block on your emails, even legitimate ones, by recipients.
>
The most common causes are:
>
the sender's email address is not valid (for example, the mailbox or domain does not exist);the message does not comply with the email sending standard (RFC 5322);the message contains links to sites often used for dangerous activities (e.g., phishing).
Updated on: 14/02/2026
Thank you!